
vacuum PAUHER
ANVISA registration number: 80223340097
DOCTOR'S AREA
WELCOME !
Here we have some useful information to assist in the removal of measurements and monitoring the treatment of their patients with Pectus Excavatum.
If you have any questions, we are available to add more help content.
Measures to define the model
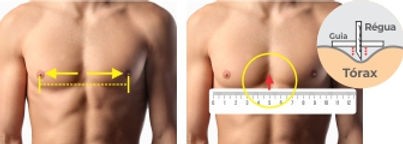
Disc model:
Measure the distance in (mm) between the two nipples and reduce 20 mm for men.
Hourglass Model:
Specially designed for women.
To measure the initial depth, use the rulers and position them so that they are below the line of the nipples and coincident with the greatest depth of the depression.

Use:
All information above and below must be validated by your responsible physician and the
period of use may vary according to diagnosis.
Add 5 minutes more during each daily use following the table below, it is important to respect the process so that your body adapts in the best way possible. If you experience severe discomfort, see your doctor in charge.
The period informed below must be applied continuously 3x a day, in the morning, afternoon and evening.
3x
to
day
WEEK 01 - 05 Minutes
WEEK 02 - 10 minutes
WEEK 03 - 15 minutes
WEEK 04 - 20 minutes
3x
to
day
WEEK 05 - 25 minutes
WEEK 06 - 30 minutes
WEEK 07 - 35 minutes
WEEK 08 - 40 minutes
WEEK 09 - 50 Minutes or more | Consult the responsible Physician
Bibliographic references on vacuum treatment, read carefully and discuss any concerns with your doctor.
- Luzia Toselli, Maxroxia Vallee, Gaston Elmo, Jorge Martinez, Daniela Sanjurjo, Maximiliano Nazar, Gaston Bellia-Munzon. Implementation and acceptance rates of a specially designed vacuometer for the vacuum bell treatment of pectus excavatum. J Pediatr Surg, 2021 Mar 19;S0022-3468(21)00211-6. https://doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2021.03.008
- Obermeyer RJ Cohen NS Kelly RE Ann Kuhn M. Frantz FW McGuire MM et al.
Nonoperative management of pectus excavatum with vacuum bell therapy: a single center study. J Pediatr Surg. 2018; 53: 1221-1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2018.02.088
- Sesia SB Hradetzky D. Haecker FM Monitoring the effectiveness of the vacuum bell during pectus excavatum treatment: technical innovation. J Pediatr Surg. 2018; 53: 411-417
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2017.05.023
- Schier F. Bahr M. Klobe E. The vacuum chest wall lifter: an innovative, nonsurgical addition to the management of pectus excavatum. J Pediatr Surg. 2005; 40: 496-500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2004.11.033
- Haecker FM Sesia S. Vacuum bell therapy. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2016; 5: 440-449
https://doi.org/10.21037/acs.2016.06.06
- St-Louis E. Miao J. Emil S. Baird R. Bettolli M. Montpetit K. et al. Vacuum bell treatment of pectus excavatum: an early North American experience. J Pediatr Surg. 2019; 54: 194-199
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2018.10.011
- Patel AJ Hunt I. Is vacuum bell therapy effective in the correction of pectus excavatum?.
Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2019; 29: 287-290. https://doi.org/10.1093/icvts/ivz082
- Togoro SY, Tedde ML, Eisinger RS, Okumura EM, de Campos JRM, Pêgo-Fernandes PM. The Vacuum Bell device as a sternal lifter: An immediate effect even with a short time use.
J Pediatr Surg. 2018 Mar;53(3):406-410. https://doi.10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2017.04.016
- Lopez M. Patoir A. Costes F. Varlet F. Barthelemy JC Tiffet O. Preliminary study of the efficacy of cup suction in the correction of typical pectus excavatum. J Pediatr Surg. 2016; 51: 183-187

